Hopefully this time we are truly on the path to truth and hope.
1 Introduction
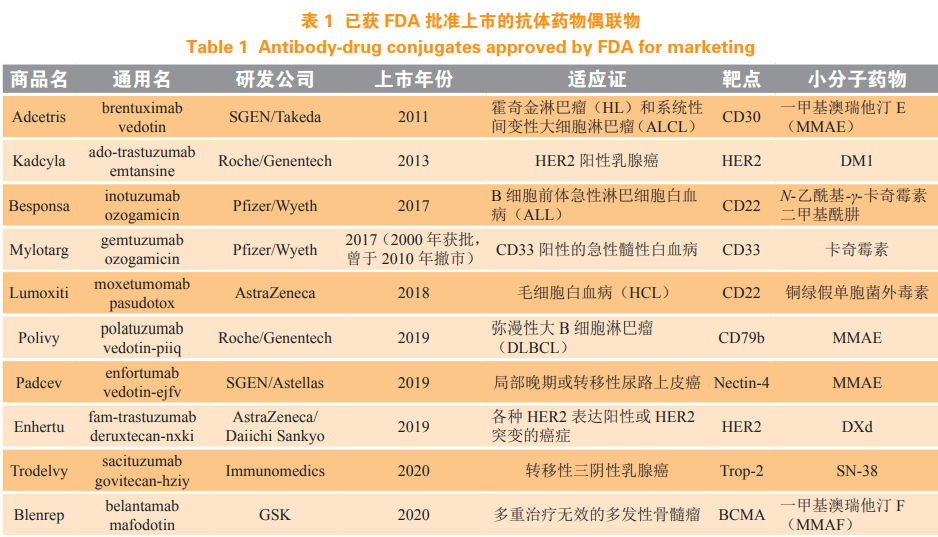
Chemotherapy is the main means of pre tumor treatment. While killing tumor cells, chemical drugs can also kill normal cells. In order to improve the tumor targeting of drugs, antibody drug conjugates (ADC) came into being. ADC Monoclonal antibodies (hereinafter referred to as McAbs) are linked to small molecule drugs by linkers (see Figure 1). With the specificity of McAbs, ADC can accurately act on the target and reduce the toxic and side effects of drugs on normal cells. ADC It has the specificity and stability of antibody drugs and the pharmacodynamic characteristics of small molecule toxins on tumor cells, and is one of the hot research directions of anti-tumor drugs at present [1-2]. Up to now, 10 types of ADC have been awarded FDA Approved for listing (see Table 1).
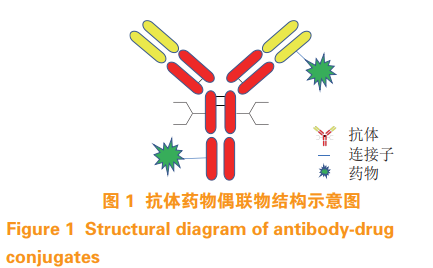
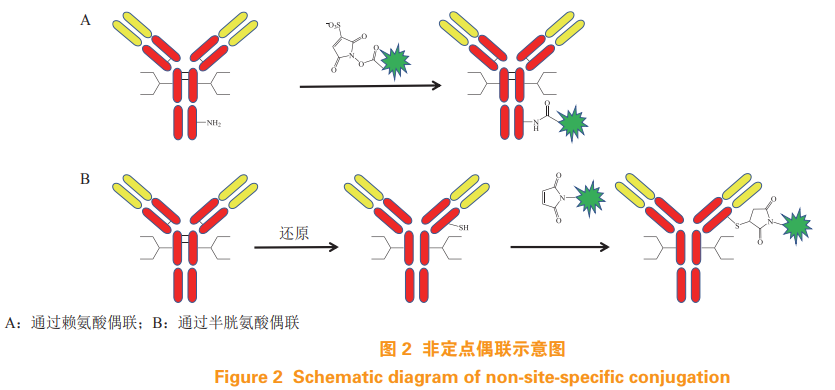
Traditional ADC The amino group of antibody lysine or the sulfhydryl group of cysteine obtained by opening the disulfide bond between chains are used for coupling, the amino group of lysine is connected with the activated carboxylate linker through amide bond, and the sulfhydryl group of cysteine reacts with maleimide group [3-4], the coupling diagram is shown in Figure 2. An antibody molecule contains 80~90 lysines, and coupling may occur in nearly 40 On different lysine residues, opening the disulfide bond between chains will result in multiple cysteine residues, which will destroy the integrity of antibody molecules. Therefore, traditional ADC It is a highly heterogeneous mixture with poor homogeneity and low stability, affecting the efficacy and therapeutic window [5]. The fixed-point coupling technology can realize the fixed-point and quantitative coupling of antibodies and small molecule toxins ADC has appropriate drug resistance ratio (DAR), high homogeneity, good stability, high reproducibility between batches, better activity and pharmacokinetic characteristics, and is more suitable for ADC Mass production [6]. This paper will review the application of fixed point coupling technology in ADC development.
2. Site directed coupling of introducing unnatural amino acids
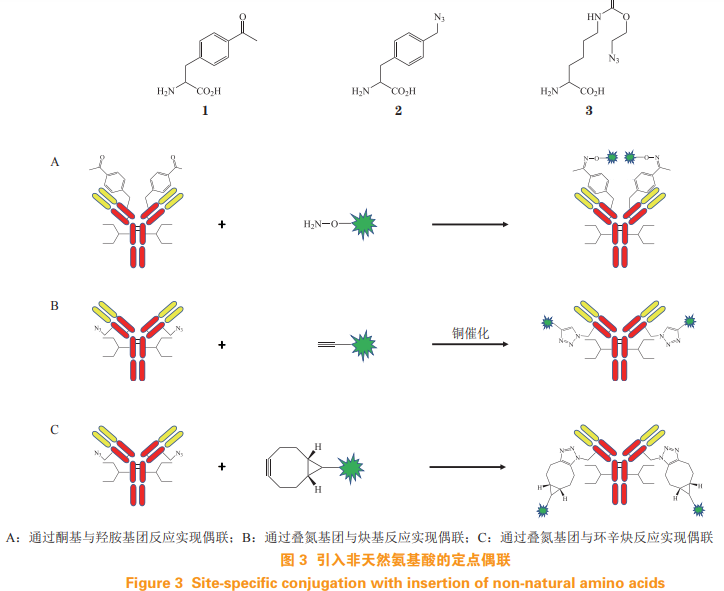
Among natural amino acids, only lysine and cysteine can be used for coupling. Non natural amino acids can be constructed into recombinant proteins to obtain residue side chains that can react with small molecule drugs. Therefore, the non natural amino acid is ADC It provides a new technical means. Antibody drug site specific coupling can be achieved through non natural amino acids. Protein synthesis on ribosomes is carried out by recognition of tRNA anti codon and mRNA codon [7]。 Ambrx introduced tRNA that can specifically recognize non natural amino acids and its corresponding aminoacyl tRNA synthetase. Under the action of aminoacyl tRNA synthetase, tRNA It combines with the corresponding non natural amino acid to form aminoacyl tRNA, and then complements the codon on mRNA through its anti codon, so that the non natural amino acid can be integrated into the polypeptide chain to synthesize recombinant antibody containing non natural amino acid [8]. The introduced non natural amino acids are usually acetylphenylalanine (1), azido methyl L-phenylalanine (2) and azido lysine (3). Keto and azide functional groups carried on non natural amino acids can react with drug linkers to obtain DAR Uniform ADC. Ketone group can form oxime bond with hydroxylamine group (see Fig. 3A), azide group can form 1,2,3-triazole cycloaddition reaction with alkynyl group under the catalysis of copper (see Fig 3B), the azide group can also combine with cyclooctyne without copper catalyst to produce azide octyne cycloaddition reaction (see Figure 3C)[9-12]。 Antibodies introduced with non natural amino acids can be linked with drug linkers in a fixed point and quantitative way to obtain DAR with uniform, high efficacy, good stability and high safety ADC, but there are also difficulties in the expression of antibodies, easy to produce immunogenicity. The ARX788 of Ambrx Company is the first antibody coupling drug developed by using non natural amino acids, which is currently in clinical research stage.
3 Enzymatic coupling
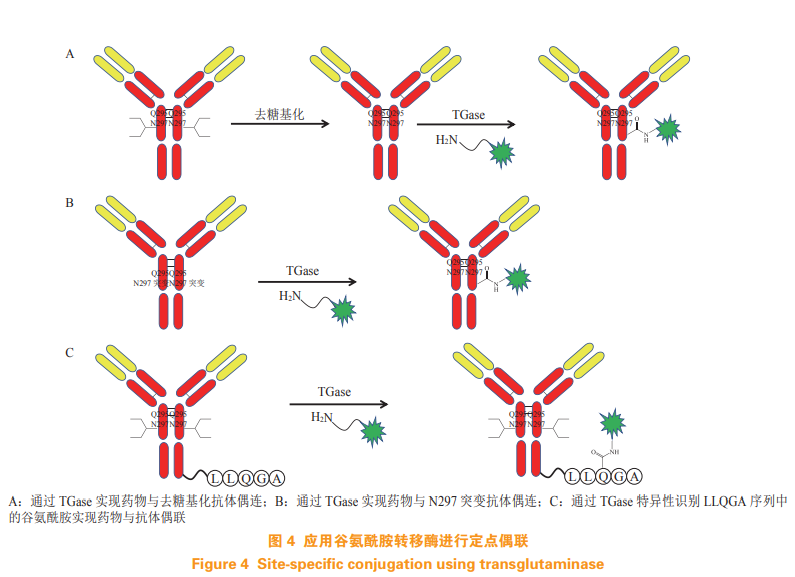
Enzymes with high specificity and efficiency are also used in With the development of ADC, antibody and small molecule drugs can be linked at a fixed point by enzymatic method. Enzymatic coupling has the advantage of site directed coupling, but it also has the potential disadvantage of immunogenicity due to the introduction of additional sequences. The following four enzymes will be The application in development is introduced. 3.1 Glutamine transferase Glutamine transferase (TGase) catalyzes the reaction of glutamine with lysine and its derivatives It can also realize the fixed-point coupling of antibody and drug. The wild type TGase transfers the amine of the drug linker to the glycosylated antibody heavy chain Q295 (see Figure 4A) [13]. Innate Pharm mutates N297, which is linked to sugar chain by antibody heavy chain, and then realizes antibody drug coupling through TGase (see Figure 4B) [14]. Pfizer proposes to insert glutamine labeled LLQGA into the antibody The pentapeptide sequence specifically recognizes glutamine in LLQGA pentapeptide sequence through TGase (see Figure 4C), and couples the drug with it [15].
3.2 Sorting enzyme
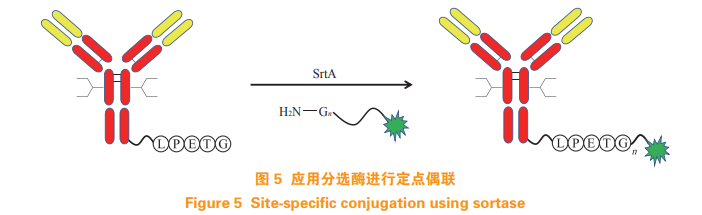
Sorting enzymes generally exist in gram-positive bacteria, which have the function of peptide transfer catalysis and can specifically recognize LPXTG Sequence, and open the peptide bond between threonine and glycine to insert the duplicate glycine sequence. Through this technology, Beerli et al. [16] inserted LPETG into the C-terminal of the heavy chain and light chain of the antibody Sequence, coupled with MMAE with glycine chain (see Figure 5), to achieve targeted coupling of antibody drugs.
3.3 Formylglycine generating enzyme
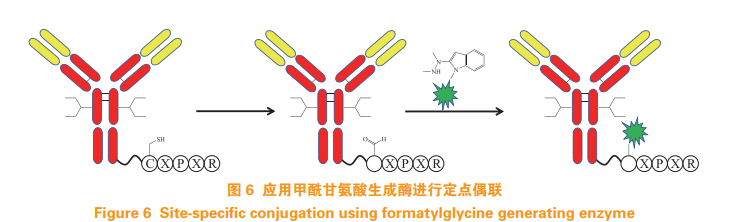
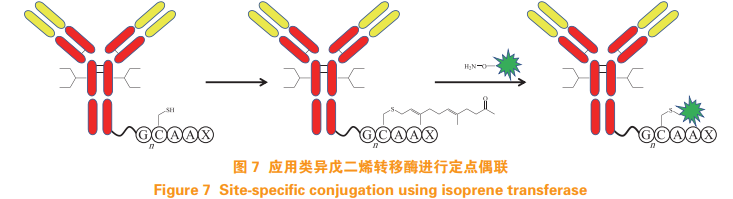
Formylglycine generating enzyme (FGE) can specifically recognize CXPXR pentapeptide sequence, replace cysteine residues with aldehyde groups, and 2 - (hydrazine methyl) - 3-indole reacts to form a stable carbon carbon bond through the synthesis of tetrahydroisoquinoline (HIPS) at near neutral pH (see Figure 6)[17]。 RedwoodBioscience's patent SMARTag ™ FGE is used to realize the fixed-point coupling of antibody and drug [18]. three point four Isoprenoid transferase LegoChemBio developed ADC using isoprenoid transferase technology [19]. Inserting CAAX linked by several glycine sequences into the C-terminal of antibody Sequence, use isoprenoid transferase to connect isoprenoyl to cysteine residue of CAAX sequence, and then carry out oxime linkage reaction with linker (see Figure 7), so as to achieve targeted coupling of antibody drugs [20].
4 Sugar chain remodeling and glycosyl coupling
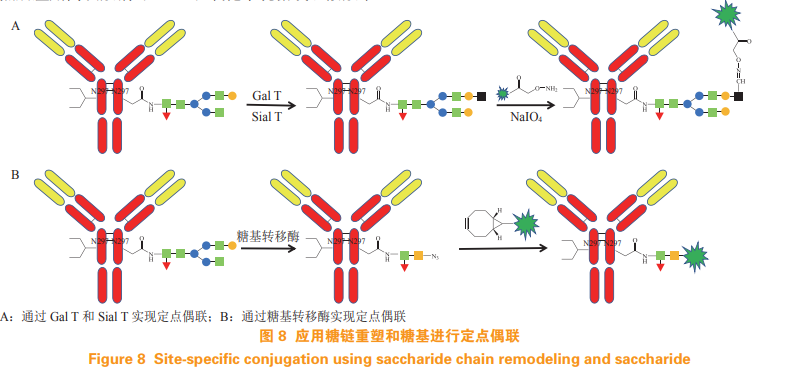
Antibody contains sugar chain in Fc segment, which can be used for targeted coupling of antibody drugs by sugar chain remodeling and sugar group. Researchers use β- 1, 4-galactosyltransferase (Gal T) and α- 2,6-sialyltransferase (Sial T) Transfer the galactose and sialic acid residues to the natural sugar group of the antibody, then use sodium periodate (NaIO4) to oxidize the cis ethylene glycol group in the galactose or sialic acid, introduce the aldehyde group, and use aldehyde to react with the molecule containing hydrazine or primary amine functional group, so as to achieve fixed-point coupling Uniform ADC of DAR (see Figure 8A) [21-22]. It is reported in the literature that azide can also be introduced by using glycosyltransferase, and stable ADC can be formed by reacting azide with cyclooctyne (see Fig 8B)[23-24]。
5. Reactive cysteine based fixed-point coupling
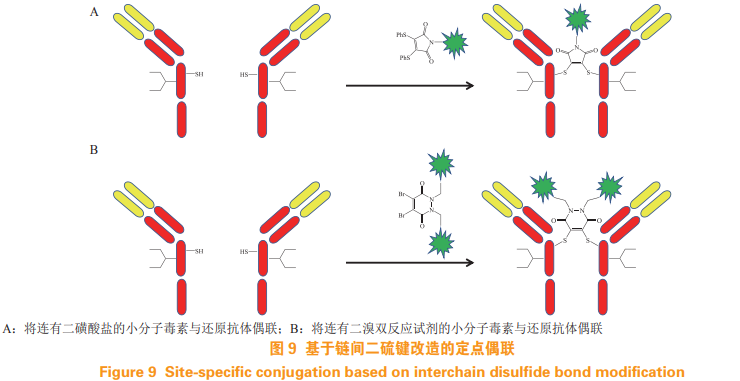
There is no cysteine residue on the antibody surface that can be used for coupling reaction, and it exists in the form of disulfide bond. For example, the most common IgG1 contains four inter chain disulfide bonds and 12 disulfide bonds in the chain. Using the traditional coupling method, first open 4 disulfide bonds between the chains to obtain free sulfhydryl groups. The DAR value of the ADC prepared by this method is 0~ 8, the homogeneity is poor. ADC determined by DAR value can be obtained by fixed-point coupling based on reactive cysteine. 5.1 Fixed point coupling based on modification of interchain disulfide bond The light and heavy chains of the antibody are connected by the interchain disulfide bond. Opening the interchain disulfide bond of the antibody has little impact on the structure and function of the antibody, and the determined reactive cysteine can be obtained. Therefore, the antibody drug can be fixed-point coupled by modifying the interchain disulfide bond. Select an appropriate reducing agent to reduce the disulfide bond between the chains of the antibody, and then connect the disulfonate (see Fig 9A) or dibromodium double reaction reagent (see Figure 9B), the small molecule toxin reacts with the reduced antibody to achieve the targeted coupling of antibody drugs [25-26]. But the ADC obtained by this method The coupling efficiency is low.
5.2 Thio Mab technology
Thio Mab was first proposed by Genentech, which is based on phage display method Mutation sites of reactive cysteine were screened on the surface. Genentech finally chose LC-V110 and HC-A114 (Kabat No.) Carry out cysteine mutation, use tri (2-carboxyethyl) phosphine (TCEP) or dithiothreitol (DTT) to only open the disulfide bond between antibody chains, and make the sulfhydryl group of the mutant cysteine in a free state, and then apply CuSO4 Or dehydroascorbic acid (dhAA) reconnects the disulfide bonds between chains, and finally reacts with the drug linker using free thiol group to achieve targeted coupling of antibody drugs (see Figure 10) [27].

5.3 Insertion of cysteine
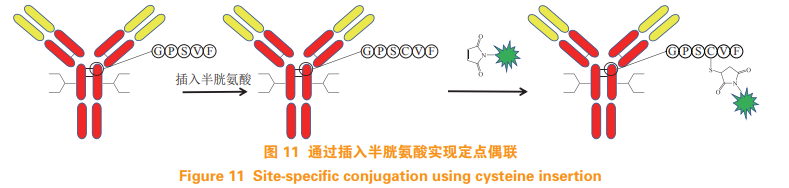
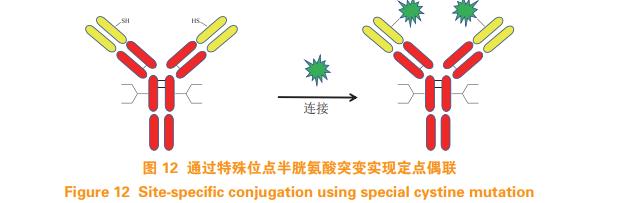
Based on the success of Thio Mab technology, Dimasi et al. [28] used the method of inserting cysteine to achieve the fixed-point coupling of antibodies and drug molecules. At the end of the heavy chain Cysteine was inserted after amino acid at position 239, mercapto group reacted with drug linker was successfully introduced, and Michael addition reaction was carried out with maleimide group to obtain ADC (see figure 11)。 The introduction of extra cysteine in this method may lead to disulfide bond mismatch. 5.4 Cysteine mutation at special sites In addition to the method of coupling with cysteine introduced above, Shiraishi et al. [29] And Shinmi et al. [30] selected a special site on the antibody for cysteine mutation, and the mutated antibody has two free sulfhydryl groups. And Thio Mab Compared with the technology, this method eliminates the reaction process of first reducing and then oxidizing, and can directly couple with the drug linker containing maleimide group to obtain ADC with DAR about 2 (see Figure 12)。 This method requires a lot of mutation sites for the modification of antibody sequence.
6 Other methods
In addition to the above fixed-point coupling methods, selenocysteine and serine cysteine can also achieve fixed-point coupling. 6.1 Selenocysteine Selenocysteine is very similar to cysteine, except that a sulfur atom in the amino acid structure is replaced by a selenium atom. The selenol group of selenocysteine is more nucleophilic than the mercaptan group of cysteine, so the antibody can be coupled under weak acidic and reducing conditions without re oxidation of the antibody. The engineered antibody obtained by inserting selenocysteine into the antibody is called "selenomabs", which can achieve the purpose of region specific coupling without changing the complete structure of the antibody [31]。 6.2 Serine cysteine McDonagh et al. [32] developed the method of serine cysteine to achieve fixed-point coupling. After opening the interchain disulfide bond, replace 4 or 6 with serine Interchain cysteine reduces the number of reactive cysteine to 4 or 2, thus generating uniform ADC.
7 Conclusion
ADC is one of the research hotspots of tumor therapy. Over the past 10 years, many types of ADC The listing drives the rapid development of ADC, and many existing ADC are in the clinical research stage. ADC also began to show more forms of monoclonal antibodies, such as nano antibody and antibody Fab Fragment, single chain variable peptide, etc; The design of linkers is also improving, and more and more small molecule drugs will be used to couple antibodies. With the development of coupling technology and the improvement of technology, ADC It will develop towards the direction of high homogeneity, high stability and high efficacy, and the prospect of cancer treatment will certainly be dark and bright.


